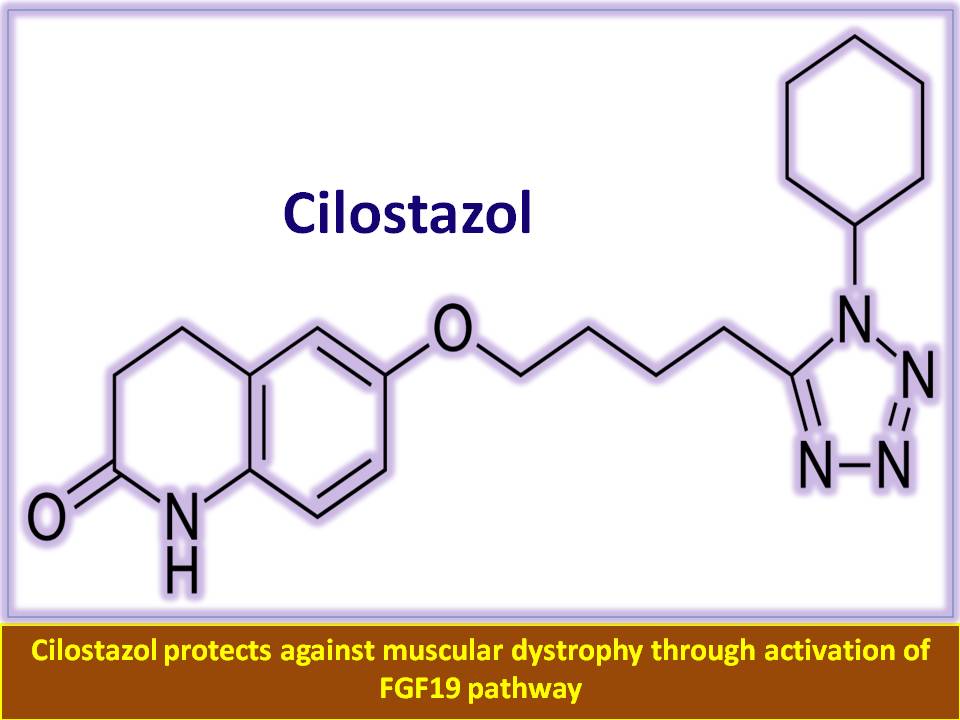
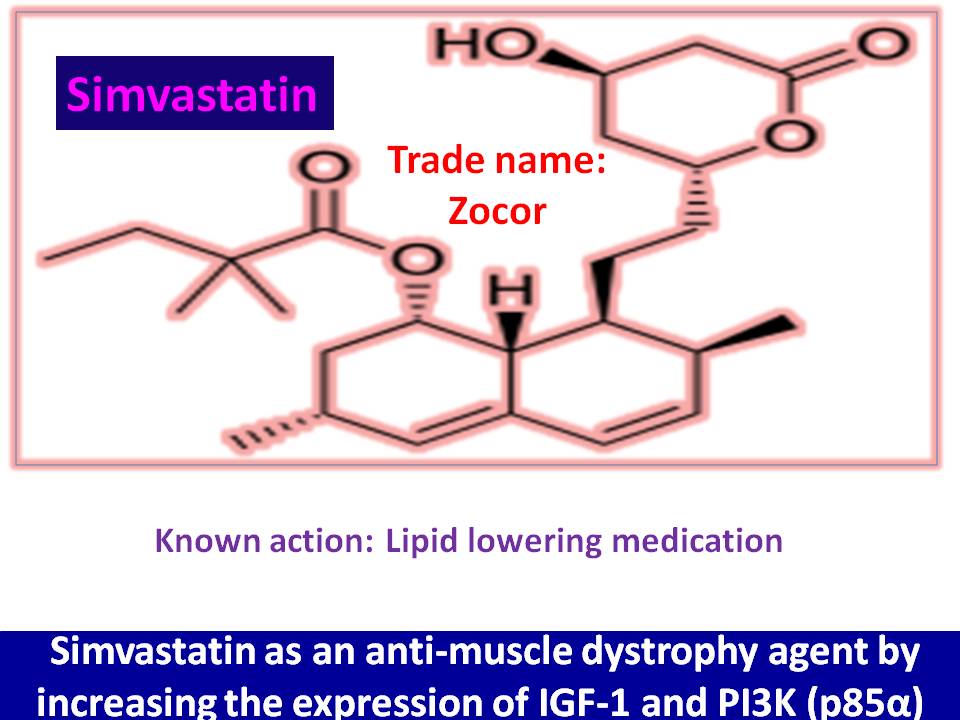
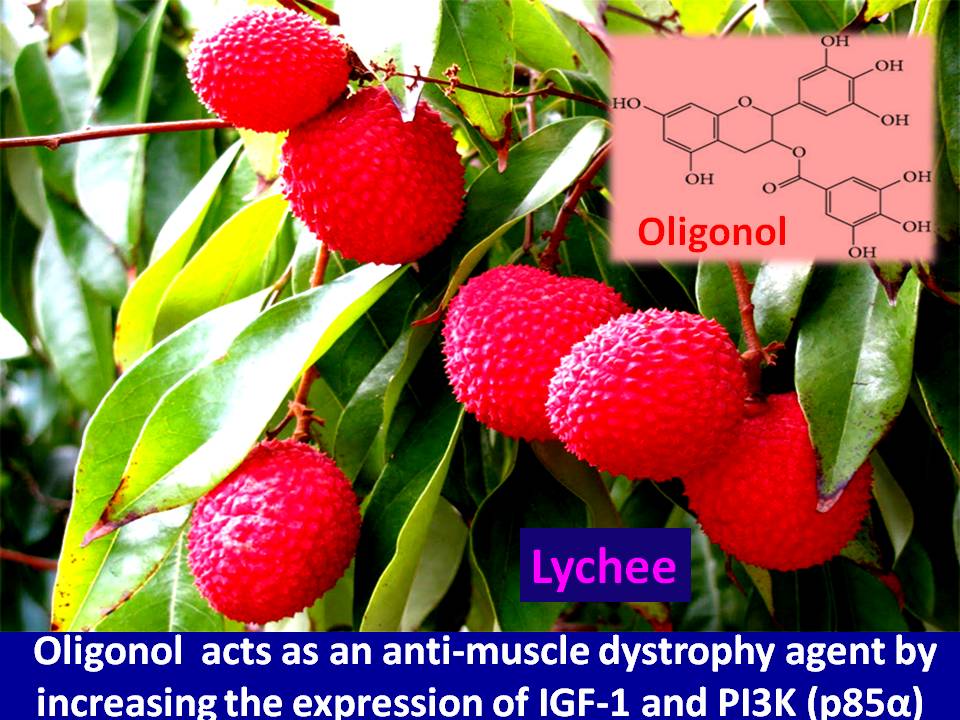
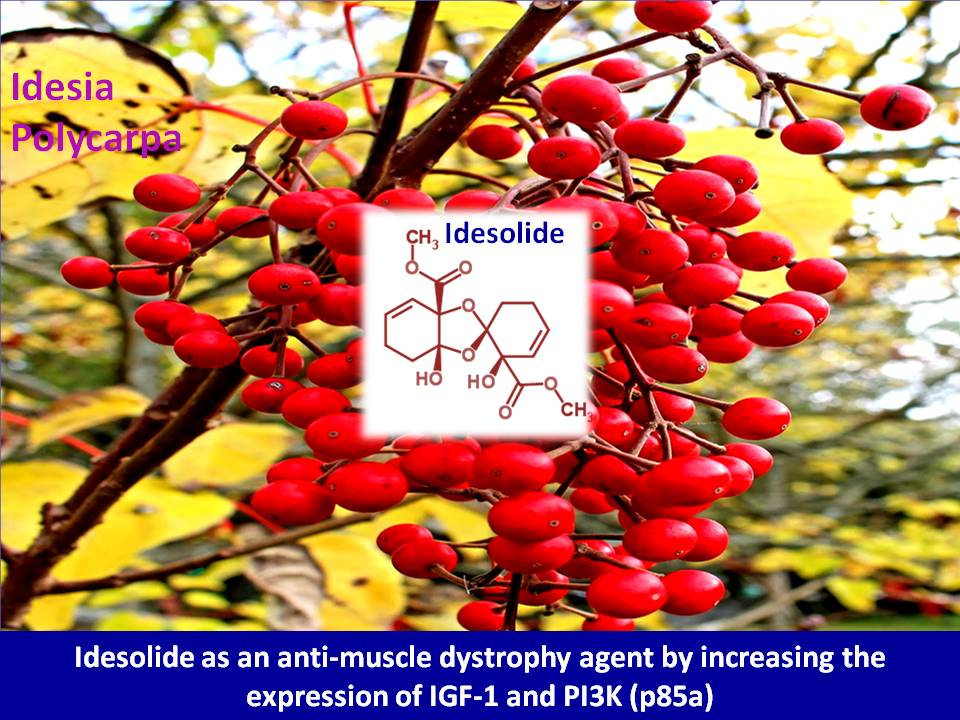
Introduction: What they say A study from Department of Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway; and Univ-Lyon, CarMeN Laboratory, INSERM 1060, INRA 1397, Université Claude Bernard Lyon, INSA Lyon, Oullins,…
read moreIntroduction: What they say A study from Department of Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway; and Univ-Lyon, CarMeN Laboratory, INSERM 1060, INRA 1397, Université Claude Bernard Lyon, INSA Lyon, Oullins, France shows that FGF19 regulates skeletal…
read moreIntroduction: What they say A study from the Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China shows that “miR-29b contributes to multiple types of…
read moreIntroduction: What they say A study from the Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China shows that “miR-29b contributes to multiple types of muscle atrophy.” This research paper was published,…
read moreIntroduction: What they say A study from the Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China shows that “miR-29b contributes to multiple types of muscle atrophy.” This research paper was…
read moreIntroduction:What they say: A recent study from Institute of Neurobiology, Institutes of Brain Science and State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, Collaborative Innovation Center for Brain Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; and Department of…
read more