The significance of the study:
Given that: (1) 15-30% of Western populations suffer from Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), while 6-25% of Asian populations suffer from it; (2) 75 to 100 million people in the US succumb to this disease; (3) obesity and type 2 diabetes are risk factor for the development of NAFLD; and (4) the global economic cost spent for NAFLD is enormous, there is an urgent need to find: (i) a way to decrease cholesterol deposition in liver; (ii) a cheaper alternative to the existing expensive drugs; (iii) a side-effect-free natural product-based drug; and (iv) a way to cure, not just treat, NAFLD.
Research findings to Therapeutic opportunity:
This study provides mechanistic insights into how a pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins may decrease lipid levels. A pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins, by increasing the expression of its target gene, it may increase the expression of HMGCR (Fig.1). Thereby, it may: (1) decrease triglycerides, free cholesterol, and total cholesterol levels; (2) decrease lipid deposition in the liver; and (3) attenuates NAFLD (Fig. 1). Thus, a pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins may used to decrease/control lipid levels/obesity/weight gain and to treat NAFLD.
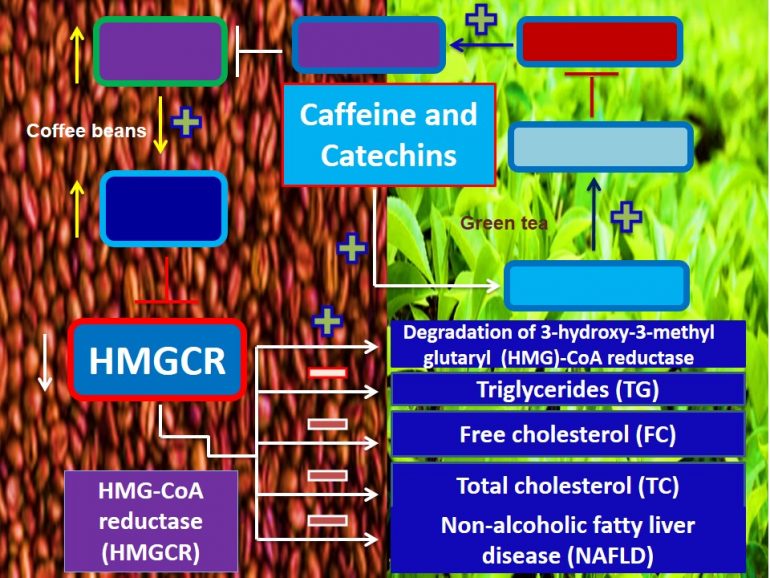
Figure 1. Mechanistic insights into how a pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins decreases the expression of HMGCR, cholesterol levels, & triglyceride levels, and attenuates the progression of NAFLD

Figure 2. Caffeine, in conjunction with catechins, decreases cholesterol and triglyceride levels and attenuates NAFLD, through downregulation of HMGCR
Details of the research findings:
Idea Proposed/Formulated (with experimental evidence) by:
Dr L Boominathan Ph.D.
Terms & Conditions apply http://genomediscovery.org/registration/terms-and-conditions/
Undisclosed mechanistic information: How does a pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins decrease the expression of HMGCR ?
Amount: $750#
# Research cooperation
For purchase and payment details, you may reach us at info@genomediscovery.org
References:
Web: http://genomediscovery.org or http://newbioideas.com (6-deoxy-L–mannose).
Citation: Boominathan, L., Mixing coffee with tea does not appear to be a tasty idea, but it will decrease lipid levels and protect against Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A pharmaceutical mixture encompassing Caffeine and catechins decreases the levels of HMGCR, triglycerides, free cholesterol, and total cholesterol and decelerates the progression of NAFLD, via up-regulation of its target gene, 15/May/2019, 12.05 am, Genome-2-BioMedicine Discovery center (GBMD), http://genomediscovery.org
Courtesy: When you cite us, kindly drop us a line at info@genomediscovery.org


