Introduction: What they say
A recent study from Research Center for Neurobiology and Department of Neurobiology, Xuzhou Medical College, 209 Tongshan Road, Xuzhou, Jiangsu 221004, PR China; and School of Public Health, Xuzhou Medical College, PR China shows that “HO-1 attenuates hippocampal neurons injury via the activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in stroke.“ This study was published, in the July 2 2014 issue of the journal Brain Research, by Prof Dong, Qi, and others.
Another study from the Department of Pharmacology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China; Department of Science and Education, Shandong Provincial Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China; and Center of Stroke, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing, China (C.-Y.M.) shows that “Regenerative Neurogenesis After Ischemic Stroke Promoted by Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Cascade” This study was published, in the June 9 2015 issue of the journal Stroke, by Prof Miao CY, Zhao Y, and others.
What we say:
On the foundation of this interesting finding, Dr L Boominathan PhD, Director-cum-chief Scientist of GBMD, reports that: A cup of Probiotic a day keeps stroke-risk at bay: Probiotic lactobacillus brevis attenuates hippocampal neurons injury, augments regenerative neurogenesis after Ischemic Stroke, and ameliorates stroke damage and neurological deficits, via up-regulation of its target genes BDNF and NAMPT
From research findings to therapeutic opportunity:
Probiotics have been found to be useful in the treatment of a number of diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease. However, the mechanism of action remains largely obscure. This study suggests, first the first time, a Probiotic lactobacillus brevis-based therapy, with detailed mechanistic insights, for stroke.
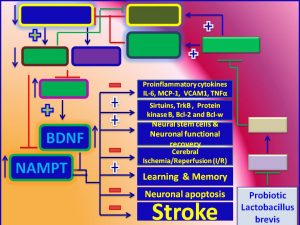
Figure 1. Mechanistic insights into how Probiotic Lactobacillus brevis against stroke. Probiotic lactobacillus brevis protects against stroke via upregulation of its target gene BDNF (Brain-derived growth factor) and NAMPT
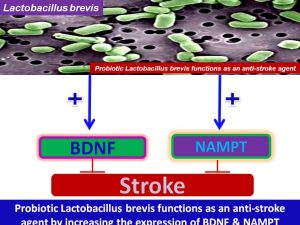
Figure 2. Probiotic lactobacillus brevis prevents stroke through induction of Brain-derived growth factor (BDNF) and NAMPT.
Probiotic Lactobacillus brevis, by increasing the expression of its target genes, it may: (1) increase the expression of BDNF and NAMPT (Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide); (2) augment neuronal–BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt–survival pathway; (3) increase sirtuins expression; (4) enhance neural stem cells; (5) promote neural functional recovery; (6) attenuate cerebral /Ischemia-reperfusion injury; (7) inhibit neuronal apoptosis; (8) improve learning and memory; and (9) attenuate neurological deficits (Figs.1-2). [easy_payment currency=”USD”]
Together, this study suggests, for the first time, that Probiotic Lactobacillus brevis may alleviate stroke, and other neurodegenerative diseases (such as multiple sclerosis, cerebral ataxia etc.), promote brain repair and extend the lifespan of an individual. Thus, Probiotic lactobacillus brevis, either alone or in combination with other drugs,” may be used to treat stroke and other neurological deficits.
Details of the idea posted:
Idea Proposed/Formulated by Dr L Boominathan Ph.D.
Terms & Conditions apply http://genomediscovery.org/registration/terms-and-conditions/
Amount: $500#
Undisclosed mechanistic information: How Probiotic lactobacillus brevis increases the expression of BDNF and NAMPT and attenuates stroke
For purchase and payment details, you may reach us at info@genomediscovery.org
# Research cooperation
References:
Citation: Boominathan, L., A cup of Probiotic a day keeps stroke-risk at bay: Probiotic Lactobacillus brevis attenuates hippocampal neurons injury, augments regenerative neurogenesis after Ischemic Stroke, and ameliorates stroke damage and neurological deficits, via up-regulation of its target genes BDNF and NAMPT, 23/September/2018, 1.22 pm, Genome-2-BioMedicine Discovery center (GBMD), http://genomediscovery.org
Courtesy: When you cite drop us a line at info@genomediscovery.org
Web: http://genomediscovery.org or http://newbioideas.com



